Setting Up a WordPress Website & Server
There’s a lot more involved than just simply installing WordPress
Setting up and maintaining a WordPress server involves several steps, from server setup to SEO optimization and ongoing maintenance. This guide provides a comprehensive walkthrough of the entire process, focusing on using cPanel in a Linux environment. Ideal for beginners, this guide will help you understand each step in detail.
1. Setting Up Your Server on cPanel
a. Choosing a Hosting Provider
- Research: Look for reputable hosting providers such as Bluehost, SiteGround, or A2 Hosting.
- Considerations: Evaluate factors like uptime, customer support, scalability, and pricing.
 b. Accessing cPanel
b. Accessing cPanel
- Login Details: Obtain your cPanel login credentials from your hosting provider.
- URL: Typically accessible via
http://yourdomain.com/cpanelor through your hosting provider’s dashboard.
 c. Creating Your Domain
c. Creating Your Domain
- Domain Registration: Purchase a domain through your hosting provider or from registrars like GoDaddy or Namecheap.
- Point Domain: Use DNS settings to point your domain to your hosting provider if purchased separately.
 d. Setting Up SSL in cPanel
d. Setting Up SSL in cPanel
- What is SSL? SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) encrypts data between your site and its visitors, which is essential for security and SEO.
- Install SSL:
- Navigate to “SSL/TLS” in cPanel.
- Choose “Install and Manage SSL for your site”.
- Use AutoSSL for free certificates or purchase one.
- Follow prompts to install.
 e. Creating an Email Account in cPanel
e. Creating an Email Account in cPanel
- Go to “Email Accounts” in cPanel.
- Create Account: Set up your email (e.g., info@yourdomain.com).
 f. Setting Up FTP Access in cPanel
f. Setting Up FTP Access in cPanel
- Go to “FTP Accounts” in cPanel.
- Create Account: Useful for manual file management.
 2. Installing WordPress in cPanel
2. Installing WordPress in cPanel
a. Using Softaculous (or Similar Auto-Installer) in cPanel
- Find Installer: Look for “Softaculous” or “WordPress” under “Auto Installers” in cPanel.
- Install:
- Choose “WordPress”.
- Click “Install Now”.
- Fill in details: site name, admin username, password, email.
- Install and wait for confirmation.
 b. Manual Installation in cPanel
b. Manual Installation in cPanel
- Download WordPress: From wordpress.org.
- Upload Files: Use FTP to upload files to your
/public_htmldirectory. - Create Database:
- Go to “MySQL Databases” in cPanel.
- Create a database and user.
- Assign user to database with full permissions.
- Run Setup: Navigate to
http://yourdomain.comto run the WordPress installation script.- Enter database info.
- Complete setup with site details.
 3. Designing Your Website
3. Designing Your Website
a. Choosing a Theme
- Navigate to Appearance > Themes in the WordPress dashboard.
- Add New: Browse free themes or upload a premium theme.
- Activate: Click “Activate” to apply the theme.
 b. Customizing Your Theme
b. Customizing Your Theme
- Go to Appearance > Customize to access the customization menu.
- Options: Modify colors, typography, layouts, and more depending on theme capabilities.
c. Installing Essential Plugins
- Go to Plugins > Add New to browse or search for plugins.
- Install and Activate:
- Page Builders: Elementor, WPBakery.
- SEO: Yoast SEO, Rank Math.
- Security: Wordfence, Sucuri.
- Performance: WP Super Cache, W3 Total Cache.
 d. Creating Pages and Posts
d. Creating Pages and Posts
- Pages: Use Pages > Add New for static pages like Home, About, Contact.
- Posts: Use Posts > Add New for blog entries.
 e. Adding Menus
e. Adding Menus
- Go to Appearance > Menus to create and manage navigation menus.
- Add Items: Include pages, posts, categories, and custom links.
- Assign Menu Location: Assign the menu to a location like the primary navigation.
 4. Optimizing for SEO
4. Optimizing for SEO
a. Setting Up SEO Plugins
- Yoast SEO:
- Go to Plugins > Add New, search for Yoast SEO, install, and activate.
- Follow the setup wizard for initial configuration.
- Use features to edit SEO titles, meta descriptions, and analyze readability.
- Rank Math:
- Similar process as Yoast SEO.
- Use the setup wizard to configure.
 b. Keyword Research
b. Keyword Research
- Tools: Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or SEMrush.
- Identify Keywords: Focus on relevant and high-volume keywords for your niche.
c. On-Page SEO
- Title and Meta Description: Craft compelling titles and meta descriptions for each page/post.
- Headings: Use H1 for titles, H2-H6 for subheadings.
- Content Optimization: Include keywords naturally in the content.
- Images: Optimize image file names and use alt text for images.
d. Technical SEO
- Sitemap: Generate and submit a sitemap via SEO plugins or third-party tools.
- Robots.txt: Configure robots.txt to control search engine access to parts of your site.
- SSL: Ensure SSL is properly installed and the site uses HTTPS.
- Speed Optimization: Compress images, use caching, and minimize CSS/JS files.
e. Off-Page SEO
- Backlinks: Aim for quality backlinks through guest posts and partnerships.
- Social Media: Promote content on social platforms to drive traffic.
f. Analytics and Tracking
- Google Analytics: Install Google Analytics to monitor traffic and behavior.
- Search Console: Use Google Search Console to track search performance and fix issues.
5. Maintaining Your Website
a. cPanel & WordPress Regular Backups
- Tools: Use plugins like UpdraftPlus or your hosting provider’s backup tools.
- Frequency: Schedule regular backups (daily/weekly).
b. cPanel & WordPress Updates
- WordPress Core: Update WordPress to the latest version regularly.
- Themes and Plugins: Keep all themes and plugins updated to avoid security vulnerabilities.
c. cPanel & WordPress Security
- Plugins: Use security plugins like Wordfence to monitor and protect your site.
- Firewall: Enable a web application firewall (WAF) if available.
- Strong Passwords: Use strong passwords and change them periodically.
d. Performance Monitoring
- Speed Tests: Use tools like GTmetrix or PageSpeed Insights to check site speed.
- Hosting: Upgrade your hosting plan if you notice performance issues.
e. Content Updates
- Review Content: Regularly update content to keep it fresh and relevant.
- Check Links: Ensure internal and external links are working.
f. User Experience
- Mobile Optimization: Ensure your site is mobile-friendly.
- Accessibility: Make sure your site is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities.
Conclusion
Creating and maintaining a WordPress website involves multiple steps, from initial server setup to ongoing SEO and performance optimization. Utilizing cPanel for server management simplifies many technical aspects, while WordPress provides a flexible platform for designing and maintaining your site. By following this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to launch a professional and efficient website.
Feel free to ask questions or seek clarification on any of the steps outlined in this guide!

 b. Accessing cPanel
b. Accessing cPanel c. Creating Your Domain
c. Creating Your Domain d. Setting Up SSL in cPanel
d. Setting Up SSL in cPanel e. Creating an Email Account in cPanel
e. Creating an Email Account in cPanel f. Setting Up FTP Access in cPanel
f. Setting Up FTP Access in cPanel 2. Installing WordPress in cPanel
2. Installing WordPress in cPanel b. Manual Installation in cPanel
b. Manual Installation in cPanel 3. Designing Your Website
3. Designing Your Website b. Customizing Your Theme
b. Customizing Your Theme d. Creating Pages and Posts
d. Creating Pages and Posts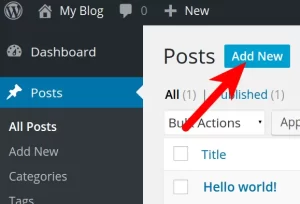 e. Adding Menus
e. Adding Menus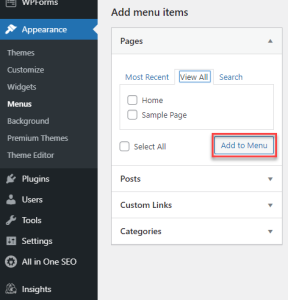 4. Optimizing for SEO
4. Optimizing for SEO b. Keyword Research
b. Keyword Research